Goaltide Daily Current Afffairs 2023
Mar 13, 2023
Current Affair 1:
PM VISHWAKARMA KAUSHAL SAMMAN (PM VIKAS)
Recently, the Prime Minister addressed a Post Budget Webinar on ‘PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman.
- About Pradhan Mantri Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman (PM VIKAS) scheme :-
- PM Vishwakarma Kaushal Samman (PM VIKAS)’ aims at improving the quality, scale and reach of products/services of artisans/craftspeople by integrating them with the domestic and global value chains.
- The scheme will enable traditional artisans and craftspeople to improve the quality, scale and reach of their products, integrating them with the MSME value chain.
- It was announced by the central government on 1 February 2023.
- It aims to increase the potential of thousands of craftspeople and artists around the nation by providing technology, skills training, and the opening of credit lines.
- The components of the scheme will include not only financial support but also access to advanced skill training, knowledge of modern digital techniques and efficient green technologies, brand promotion, linkage with local and global markets, digital payments and social security.
- It will greatly benefit the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, OBCs, women and people belonging to the weaker sections.
- Will give impetus to the MSME sector and empower the Vishwakarma community.
Current Affair 2:
MSME COMPETITIVE (LEAN) SCHEME
- Union Minister for MSME launched the MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme recently.
About MSME Competitive (LEAN) Scheme:-
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises, Government of India.
- E- Certificate towards participation under the scheme will be issued by MoMSME after completion of Basic Level, Intermediate Level, and Advanced Level.
- Aim: It aims to enhance their productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness by reduction of wastage in processes, inventory management, space management, energy consumption, etc.
- Eligibility: All MSMEs registered with the UDYAM registration portal will be eligible to participate. Also open to SFURTI and Cluster Development Program Schemes.
- Funding: Central government will contribute 90% of the implementation cost for handholding and consultancy fees.
- An additional contribution of 5% for the MSMEs which are part of SFURTI clusters, owned by women/SC/ST and located in the North-East Region
- Benefit: MSMEs can reduce wastages substantially, increase productivity, improve quality, work safely, expand their markets, and finally become competitive and profitable
- Components of Schemes: –
- Industry Awareness Programmes/Workshop: MSMEs will be made aware of the Scheme through Nationwide awareness programmes.
- Training Programmes: Stakeholders like the MSME Officers, Assessors and Consultants will be trained
- Handholding: MSMEs will be provided handholding towards the implementation of Lean Tools and Techniques at three different levels – Basic, Intermediate, and Advanced.
- Benefits/Incentives: Graded incentives will be announced by the Ministry of MSME for MSMEs for encouraging MSME units’ participation under the scheme.
- The PR campaign, Advertising & Brand Promotion: For popularizing the Lean Scheme, nationwide publicity will be done.
- Digital Platform: Lean Scheme process will be e-enabled through a single window digital platform.
- Under the scheme, MSMEs will implement LEAN manufacturing tools like 5S, Kaizen, KANBAN, Visual workplace, Poka Yoka etc under the able guidance of trained and competent LEAN Consultants.
Current Affair 3:
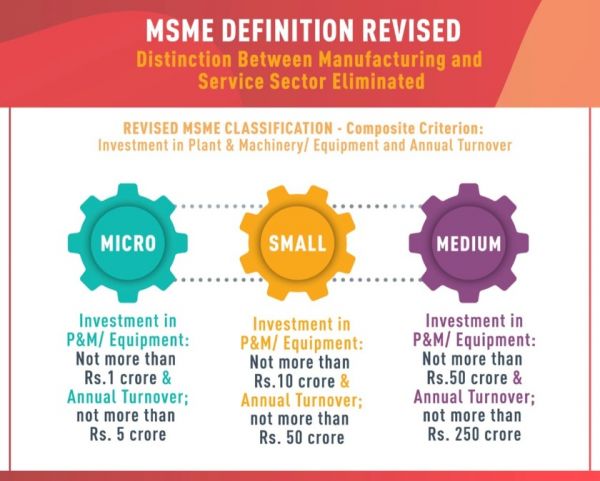
NET-ZERO WASTE TO BE MANDATORY FOR BUILDINGS
- According to the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, all upcoming housing societies and commercial complexes in the country will soon mandatorily have to ensure net zero waste.
Background
- The directive is part of the Manhole to Machine-hole scheme for the complete removal of manual scavenging and has been formulated as a convergence of programmes like Swachch Bharat, NAMASTE and AMRUT.
- India currently generates 72,368 million litres per day of urban wastewater of which only 28% is treated.
- According to a 2021 report – ‘Circular Economy in Municipal Solid and Liquid Waste’, if the sale of treated sewage is institutionalised, it can add close to ₹3,285 crore annually.
- The UN SDG 6.3 aims at halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally by 2030.
- What does achieving net zero waste mean?
- Reducing, reusing, and recovering waste streams (sludge) to convert them to valuable resources so that zero solid waste is sent to landfills.
- Net zero waste along with the treatment of liquid discharge will be part of the government’s push for reforming and modernising the sewage disposal system.
Current Affair 4:
LANDSLIDE ATLAS OF INDIA
- Recently, the Indian space Research Organisation (ISRO) has released the Landslide Atlas of India.
About Landslide
- Landslide is a rapid movement of rock, soil, and vegetation down the slope under the influence of gravity.
- Landslides are caused due to three major factors: geology, morphology, and human activity.
- Causes of landslide:-
- Rainfall and Snowfall- The occurrence of heavy or continuous rainfall may lead to heavy landslides in the areas of steep slopes where National Highways and roads have been constructed.
- Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions-Earthquakes are the most important cause of landslides in the folded mountainous areas. In India, Landslides are more frequent in the folded mountains of the Tertiary Period, like the Himalayas.
- Mining, Quarrying and Road cutting- The continuous extraction of coal, minerals, and stones from the mines and quarries and the development of roads by cutting the steep slopes in the folded mountains create conducive conditions for the occurrence of landslides.
- Loading by construction of houses- The unplanned growth of towns and cities in the hilly areas without testing soil and rocks in also an important cause of landslides.
- Deforestation- Deforestation and other human activities also induce landslides.
- Landslide-Prone Areas in India:-
- Himalayan tract, hills/mountains in sub-Himalayan terrains of North-east India, Western Ghats, the Nilgiris in Tamil Nadu Konkan .
- Important Highlights from the ‘Landslide Atlas of India’
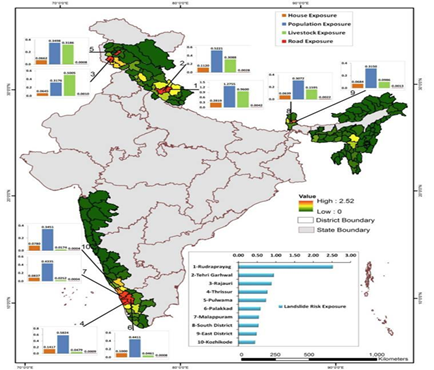
- India’s vulnerability to landslides: India is among the top four countries with highest landslide risk, where for every year the estimated loss of life per 100 km2 is greater than one.
- Approximately 0.42 million sq. km or 12.6% of land area of India, excluding snow covered area, is prone to landslide hazard.
- In India, landslides mostly occur in the monsoon season. Himalayas and Western Ghats are highly susceptible to mass movements due to hilly topography and heavy rainfall.
- Most vulnerable districts: Rudraprayag and Tehri Garhwal in Uttarakhand are the most landslide-prone districts in the country.
- Rajouri, Thrissur, Pulwama, Palakkad, Malappuram, South Sikkim, East Sikkim and Kozhikode in Kerala, Jammu Kashmir and Sikkim are other high-risk districts, found the Atlas.
- Maximum landslides: Between 1988 and 2022, the maximum number of landslides — 12,385 — were recorded in Mizoram.
- Uttarakhand followed it at 11,219, Tripura at 8,070, Arunachal Pradesh at 7,689, Jammu and Kashmir at 7,280.
About the Landslide Atlas of India 2023
-
- About Landslide Atlas of India:- It is a database of landslide-prone regions of India based on events during 1998 – 2022.
- It is created by the National Remote Sensing Centre, ISRO Department of Space, Government of India
- In addition to aerial images, high-resolution satellite images captured using ResourceSat-1 and 2, etc., were used to study the landslides.
- This Atlas provides the details of landslides present in Landslide provinces of India
- The database covers landslide-vulnerable regions in 17 states and 2 UTs of India in the Himalayas and Western Ghats.
- The database includes three types of landslide inventory – seasonal, event-based, and route-wise for the 1998-2022 period.
- The technology used: Satellite data of high to very high resolution such as IRS-1D PAN+LISS-III, Resourcesat-1, 2 and 2A LISS-IV Mx, Cartosat-1 and 2S, data from International satellites (Sentinel-1&2, Pleiades and WorldView) and Aerial images were used in the mapping of landslides.
- Vulnerability Ranking: The database was used to rank 147 districts in 17 states and 2 UTs of India for their exposure to landslides in terms of key socio-economic parameters.
Steps taken by the government:-
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) has done a national landslide susceptibility mapping for 85% of the entire 4,20,000 square km landslide-prone area in the country.
- The areas have been divided into different zones according to the propensity of the disaster.
- NDMA Guidelines for Landslides –
- Landslide Hazard, vulnerability and Risk Assessment
- Multi – Hazard Conceptualization
- Landslide Remediation practice
- Research and Development, monitoring, and early warning
- Knowledge network and management
- Capacity building and Training
- Public awareness and Education
- Emergency preparedness and response
- Regulation and Enforcement
Current Affair 5:
INDIA, BRAZIL, SOUTH AFRICA (IBSA)
- A recent report highlighted that India, Brazil, South Africa can play vital role in reforming digital governance.
About IBSA
- IBSA brings together India, Brazil, and South Africa, three large democracies and major economies from three different continents, facing similar challenges.
- Background : Its genesis can be traced back to the decades of efforts by countries and groupings working together to ensure South-South solidarity such as the Bandung conference in 1955, the Non-Aligned Movement in 1961, the G77 grouping, UNCTAD, the Buenos Aires Plan of Action 1978, and the 2009 Nairobi declaration.
- Formation : The grouping was formalized and named the IBSA Dialogue Forum when the Foreign Ministers of the three countries met in Brasilia in June 2003 and issued the Brasilia Declaration.
- Five IBSA Leadership Summits have been held so far.
- The 5th IBSA Summit was held in Pretoria in October 2011.
- India convened the 6th IBSA summit under the theme “Democracy for Demography and Development” in 2021.
- IBSA does not have a headquarters or a permanent executive secretariat.
- IBSAMAR (IBSA Maritime Exercise)
- Cooperation in IBSA is on three fronts: first, as a forum for consultation and coordination on global and regional political issues second, trilateral collaboration on concrete areas/projects and third, assisting other developing countries by taking up projects in the latter through IBSA Fund.
- The IBSA facility for poverty and hunger alleviation (IBSA Fund) was established jointly by India, Brazil, and South Africa in March 2004.
- The IBSA Visiting Fellowships Program was instituted, with the financial support of the Ministry of External Affairs, Government of India in 2016
<< Previous Next >>



